Our manufacturing capabilities
Optical spherical components
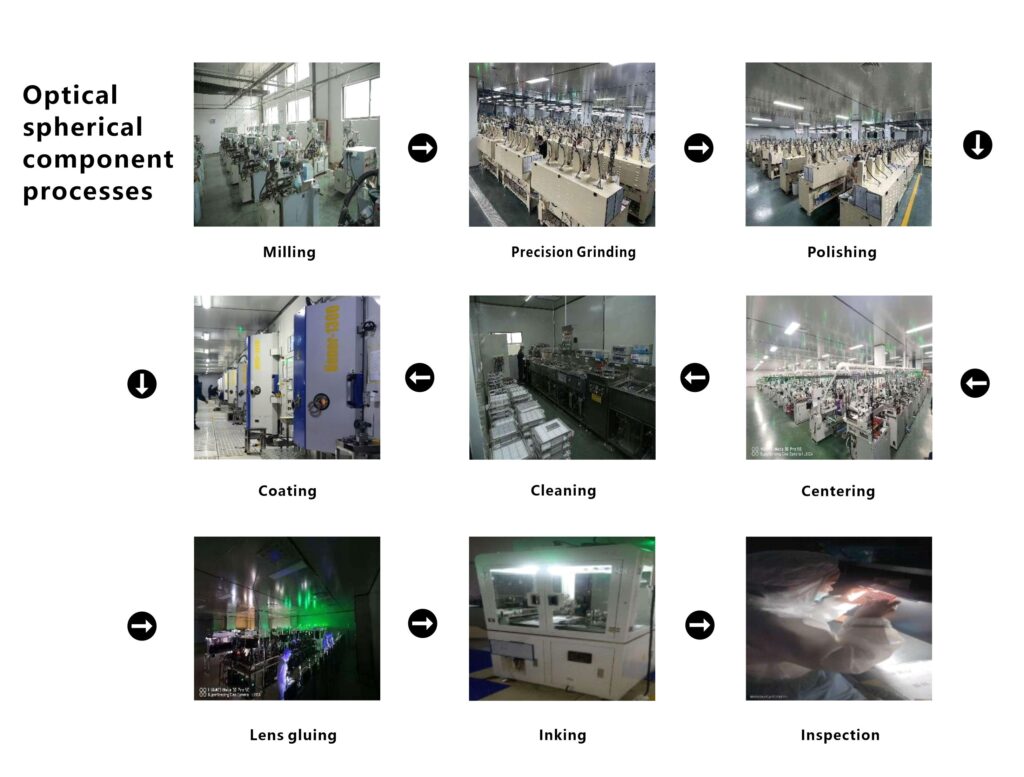
Optical spherical components are crafted with meticulous attention to detail, with strict control over every step of the manufacturing process. The main processes include milling and grinding, fine grinding, polishing, coring, coating, cementing, and edge blackening.
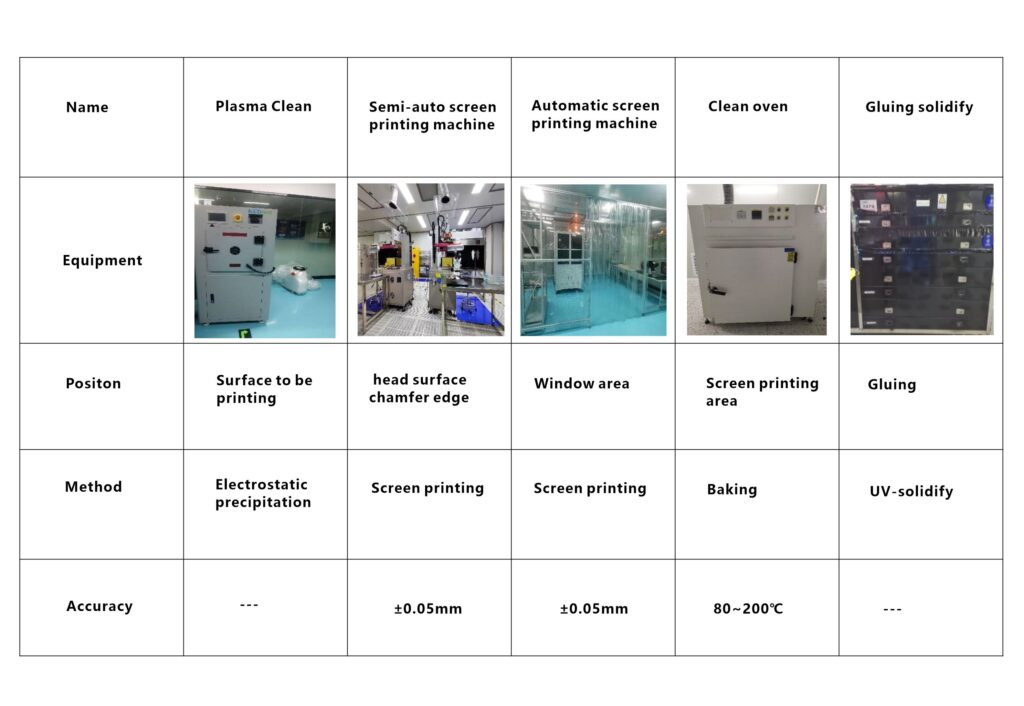
The company all purchased Japan imported OPTRUN coating machine (40 sets), with OTFC, OTFG, GENER, DSC-1650U SPUTTERING models, equipped with planetary wheel, high-energy ion source, Continuous sputtering coating machine. Can process anti-reflection film, plus hard film, super hard waterproof film, hydrophilic film, filter film, anti-oil anti-fog film and special infrared, ultraviolet film. Our coating team has more than ten years of coating experience. In the ultra-low anti-reflection coating (420-680nm, R<0.15%), the vehicle anti-fog film (double 85-1000 hours), reaching the industry leading level.
Advanced equipment, superb technology and strict management ensure that the film system can meet the strict requirements of the on-board lens reliability test.
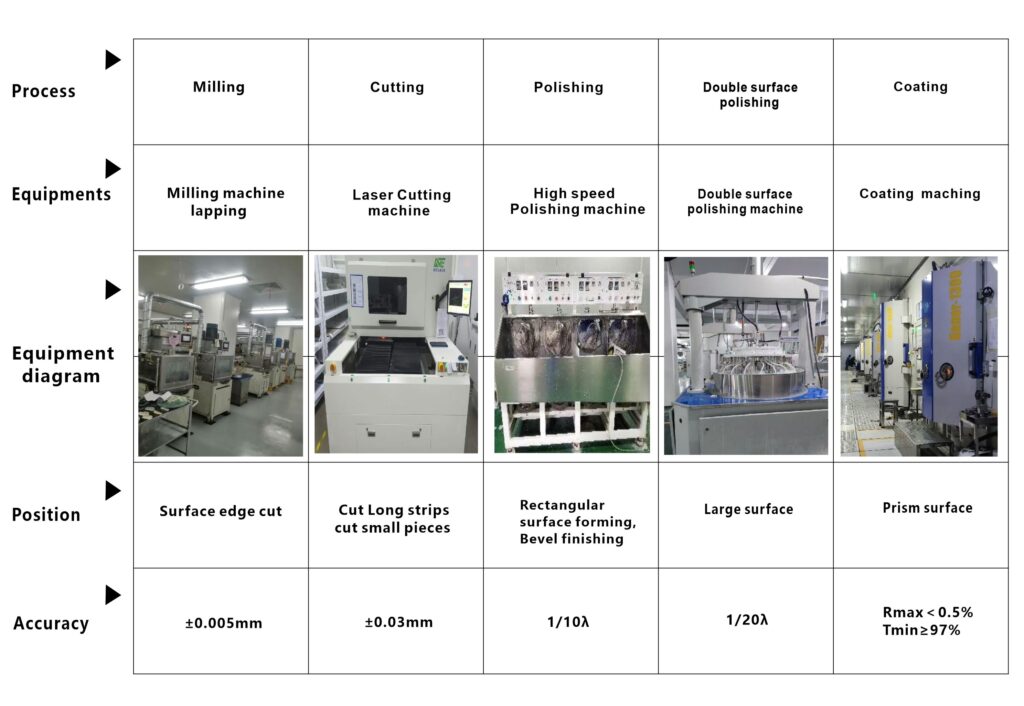
Optical spherical component processing capability
Diameter 2~80mm, tolerance:±0.003mm
Mass production level achieved in the industry : ±0.005mm
Transcore Decentration:30″ ,Industry mass production level 60″
N:±1; Radius:0.68-∞
ΔN:0.3; Thickness:±0.01mm,Industry mass production level ±0.015mm
Abrasion hardness:60~80 Hard material,>400 Soft material
Gluing decentration:30″,Industry mass production level 60″
Inking overflow requirement:0.15mm
Prism processing key processes and equipments
The company’s core technical team has long been engaged in the development and manufacturing of optical components. They have received extensive training from Fujinon and Konica Minolta, both in Japan (Sano factory) and Shanghai. We have mass production experience with beam splitters, mirrors, light guides, PSCs, color-combining prisms, DLP prisms, and lenses for interchangeable lenses.
High-Precision Automation Empowers Optical Lens Manufacturing for Superior Imaging Performance
🔧 Precision Assembly: Micron-Level Accuracy with Robotics
We utilize high-precision robotic systems to achieve micron-level pick-and-place operations in security and automotive lenses. This ensures precise alignment of each optical element, significantly enhancing overall image quality—especially critical for high-demand recognition in complex traffic and surveillance scenarios.
🧪 Automated Gluing and Component Integration
Robots precisely dispense and cure UV adhesive to form robust lens assemblies that withstand wide temperature fluctuations and intense vibrations. They also integrate focusing mechanisms and aperture components to ensure stable coordination between optical and mechanical functions.
🔍 Intelligent Autofocus and Image Optimization Testing
Through automated focusing systems and image recognition algorithms, the system simulates various lighting and distance conditions to optimize lens sharpness. This ensures clear imaging at all ranges for security lenses and rapid focus capabilities for automotive applications.
📊 Multi-Dimensional Optical Performance Testing
Systematic testing of resolution, distortion, chromatic aberration, transmittance, and optical loss guarantees high resolution, low distortion, and true-to-life visuals, meeting the demands of precise imaging under complex lighting conditions.
🌡 Extreme Environment Reliability Verification
All lenses undergo vibration and thermal cycling tests before delivery to ensure long-term reliability in automotive environments with intense shocks and temperature shifts, as well as continuous outdoor use in security applications.
Reliability guarantee – can meet experimental conditions
(nO.)(test Items)
(测试条件)
NO.1:(High temperature and high humidity test)
Stored at +85°C, 85% RH for 1500 hours, followed by 2 hours recovery at room temperature before testing.
NO.2:High Temperature Storage Test
The test article was stored at +105°C for 1440 hours, followed by 2 hours of recovery at room temperature before testing.
No.3:Low Temperature Storage Test
The test article was stored at -40°C for 1500 hours, followed by 2 hours of recovery at room temperature before testing.
No.4:Thermal Shock Test /Ice Water Test
The lens was placed in a temperature cycling chamber at room temperature. The chamber was set to alternate between +110°C for 0.5 hours and -40°C for 0.5 hours, with a 30-second transition time, for a total of 1000 cycles.
No.5:Abrasion Resistance Test
Test Method 1:
Apply a pressure of 20 N (2.04 kg) using a brown bristle brush and rub back and forth on the lens surface 1000 times.
Test Method 2:
Mix 100 g of Kanto silt with 1 L of water. Soak a car wash sponge in the mixture, apply a 500 g load, and rub the surface of the test sample 500 times. Since the silt tends to settle, the mixture must be stirred regularly.
Test Method 3:
Using an HB pencil, apply a force of 1.0 kgf/cm² and perform 500 strokes back and forth on the surface of the top lens.
Test Method 4:
Use a ruler and utility knife to score the test piece with 1 mm spacing until a 100-grid pattern is formed. Then apply 3M tape and peel it off three times at a 45° angle.
No.6:Salt spray test
Temperature: 35°C, salt solution concentration: 5%, pH maintained at neutral (pH = 6.5–7.2). Exposure duration: 1000 hours.
No.7: Aging test/Xenon lamp test
Tested according to AEEJ 2527 standard for 1000 hours.
No.8:Steel ball drop test
A 50g steel ball was dropped freely from a height of 20 cm onto the lens surface once, and the lens did not crack.
No.9:Corrosion resistance test
No.10: Acid resistance test
The test piece was immersed in a pH 1 H₂SO₄ solution for 2 hours.
No.11: Chemical resistance
Liquid/Spray:
The front of the lens is immersed in a 6×6 cm cotton towel moistened with 10 ml of the corresponding reagent for 1 hour, then air-dried for 15 seconds, and subsequently stored at the baking temperature specified in the attached schedule for 48 hours. After the test, all specifications must be met.
Paste:
The front of the lens is coated with 5 g of the corresponding reagent, air-dried for 1 hour, then stored at the baking temperature specified in the schedule for 48 hours. The test result must meet all specification requirements.
Solid:
A cotton swab is used to pick up the corresponding solid reagent and rubbed on the front of the lens for 15 seconds, then left in air for 1 hour, followed by storage at the baking temperature specified in the schedule for 48 hours. After the test, all specifications must be met.
The types of chemical reagents refer to the chemical test standard.
No.12: Sweat resistance test
Take an A4 printer paper and lay it neatly on the test desktop.
Take a piece of TA9008 dust-free cloth and place it in a beaker. Use a measuring cylinder to measure 18 ml of prepared acidic sweat and evenly drop it onto the dust-free cloth. Then take out the cloth and lay it flat on the A4 printer paper.
Place the test sample on the dust-free cloth.
Wrap the test sample upside down with the dust-free cloth.
Fold the excess dust-free cloth extending from the top and bottom sides onto the test sample.
Transfer the wrapped test sample horizontally into a PE bag.
Repeat steps 2 to 6 until all acidic sweat test samples are wrapped.
Clean the test desktop and replace the A4 printer paper. Replace the test sweat with alkaline sweat and repeat steps 2 to 7.
Continue until all alkaline sweat test samples are wrapped. The PE bags containing alkaline sweat samples must be kept separate from those containing acidic sweat samples.
Place all test samples into a temperature and humidity chamber set at 55°C and 95% RH for 120 hours.